

You can feel too tired and weak to move around as much. So you don’t need to have needles into your hand or arm each time you have cancer drug treatment.Ĭancer and its treatment can make you feel very ill. These lines usually stay in your veins for many months. They make sure the benefits of these treatments outweigh the risks.īlood clots can also form in long lines such as central lines and PICC lines. Your doctor will explain if the treatments you are having increase the risk of blood clots.
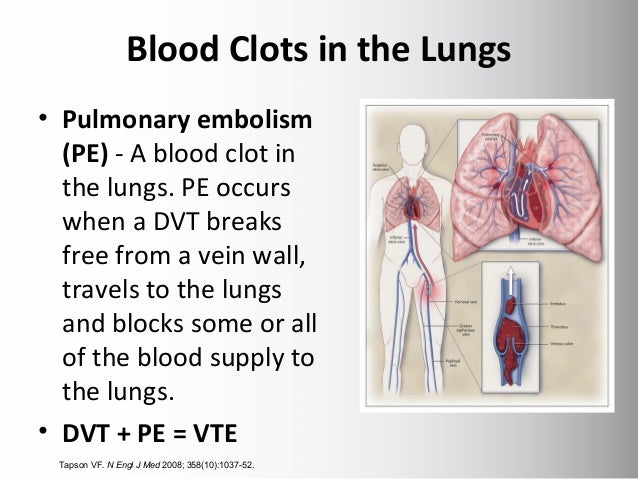
They combine with platelets to form blood clots and help us stop bleeding. This may be because cancer cells make chemicals that stimulate the body to produce clotting factors.Ĭlotting factors are proteins made naturally by the liver. People with cancer often have sticky blood. Researchers think that up to 20 out of every 100 people with cancer (up to 20%) develop a blood clot at some point. People with cancer have a higher risk of developing blood clots. pain in your chest or upper back which gets worse when you breathe inĬall 999 or go to A&E if you have symptoms of a blood clot in your lungs.feeling breathless - this might start suddenly or increase over time.If a blood clot has moved to your lungs (a pulmonary embolism), the symptoms include: redness and swelling in your leg - this may be just in the calf or include the whole of your leg.So it's important to know about the symptoms of blood clots and report them to your doctor or nurse immediately. DVTs and PEs together are sometimes called venous thromboembolism (VTE).ĭoctors can successfully treat most blood clots when diagnosed. If this happens, it’s called a pulmonary embolism (PE). It may travel through your heart to block part or all of the blood supply to the lungs. Part or all of a DVT can break off and travel around the body.

When a blood clot forms in the deep veins of the leg it is called a deep vein thrombosis (DVT). The medical name for a blood clot is thrombus.īlood clots can develop in different parts of the body. What is a blood clot?Ī blood clot is a collection of blood that can form inside a blood vessel (a vein or an artery). Contact your doctor or get advice from 111 if you think you have a blood clot. They may be more likely to suggest this if there is a family history of pulmonary embolism or deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and if you are due to stop anticoagulation treatment.Blood clots can be very serious. But in certain circumstances if you have a confirmed diagnosis of pulmonary embolism, your doctor may recommend a blood test to look for inherited conditions which increase the risk of clots. Routine testing for genetic risk of blood clots is not recommended. Cancer treatments such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy can also increase the chances of blood clots. Less commonly, you might have a condition that causes your blood to clot more easily than normal, such as cancer.
BLOOD CLOT LUNGS CAUSE PROFESSIONAL
Your chances of developing a blood clot are very small if you’re taking the contraceptive pill or HRT, and your health care professional will consider your individual risk before they prescribe them. take some forms of hormone-based contraception or hormone replacement therapy (HRT).are pregnant – your risk is increased for up to six weeks after giving birth.Some people are at a higher risk of blood clotting which can cause a pulmonary embolism.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
